Purpose
of Drawing:
The
purposes of drawing are to improve the uniformity of the slivers and to
straighten the fibres in the slivers. The improvement in uniformity is due to
the doubling and drafting of eight to ten slivers can into one. The
straightening of the fibres is accomplished by drawing fibres by each other.
The straightening is important because it arranges the fibres more parallel to
each other and to the direction of the fibre strand. When the fibres are well
straightened, the arrangement helps in producing uniform, strong and smooth
yarn.
Objectives of Draw Frame Machine:
v To
straighten the curled and hooked fibres.
v To make the
fibres parallel to their neighboring fibres.
v To improve
uniformity of fibres by drafting and doubling.
v To reduce mass
per unit length of sliver.
v To remove
micro dust from slivers by air suction pipe.
v To blend
raw material perfectly.
TYPE OF DRAW FRAME:
1.
Breaker
Draw frame: Feed material is carded sliver. During this process 8-10
carded slivers are fed to this machine to produce more parallelized breaker
sliver.
2.
Finisher
Draw frame: Feed material is breaker draw frame drawn sliver. During
this process 8-10 breaker slivers are fed to this machine to produce more parallelized
& uniformed finisher sliver.
Operating
Principle
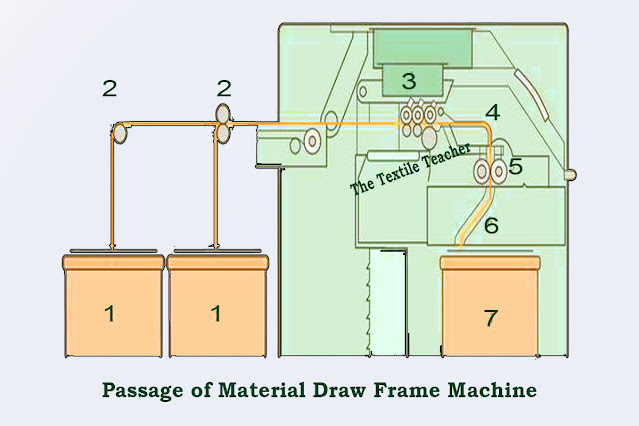
The passage of material of Draw Frame
machine is Eight to ten card or draw frame slivers (see Fig. Passage of Material
Draw Frame Machine) are fed to the drafting zone (3). A feed
roller pair (2) is located above each can (1) to enable the
feeding step to be performed in a controlled manner without false drafts. The
feed roller pairs are mounted in a creel zone and each is positively driven.
The slivers running into the drafting zone leave it, after a draft of 8 to 10,
as a web lacking significant cohesion. In order to avoid disintegration of the
web, which would otherwise be unavoidable at the high operating speeds
currently in use, it is condensed into a sliver immediately after the drafting
arrangement. This sliver is then (for example in some makes) guided through a
tube (4) via a passage (6) of the sliver tube into a can (7),
in which it must be laid in clean coils with optimal utilization of the space
in the can. To enable the can to take up as much material as possible, the
sliver is compressed by passing it through calendaring rollers (5).
DIFFERENT ZONES OF DRAW
FRAME MACHINE
CREEL ZONE
It is known
as feeding zone. 8-10 feed slivers passing through guide roller, guide bars
& feed to drafting zone.
GUIDE ROLLER:
It guides
the passage of feed slivers and act as a stop motion when feed sliver breaks
AUTO LEVELER:
The main task of auto leveling is to eliminate deviations in
mass per unit length.
Auto
leveler is an additional device which is meant for correcting the linear
density variations in the delivered sliver by changing either the main draft or
break draft of the drafting system, according to the feed variation.
DRAFTING ZONE
Definition of Draft is the measure of the amount the sliver
is reduced (reduce mass per unit length) as it passes through the machine. The
draft on draw frames may be determined by the ratio of mass fed and delivered. The
draft takes place in drafting zones (Drafting Rollers). The fibres are held
firmly between the top roller and bottom rollers. It is the zone for a process of
decreasing the weight per unit length of sliver. It is mainly due to
differential peripheral speed of the rollers.
SLIVER COILING:
The rotary movements are required for coiling
of the sliver. On the one hand, the rotatable plate must be rotated above the
can, while the can itself must rotate, at a considerably slower rate, below the
plate. A sliver tube is provided on the plate as a fixed part to guide the
sliver from the calendar rollers into the can.
DOFFING OF CANS:
In Single-step changers full cans are replaced
by empty ones at full speed, i.e. without stopping the machine. In
Multiple-step changers machine is brought to a stop during the change.
·
THE TASK OF THE DRAW FRAME
EQUALIZING
One of the main tasks of the draw frame is improving
evenness over the short, medium and long term. Card slivers fed to the
draw frame have a degree of unevenness that cannot be tolerated in practice, and
slivers from the comber contain the infamous piecing’s;
these must be obscured. It should be noted, however, that short-wave sliver
evenness is not as sometimes assumed the sole criterion for evaluating the performance
of the draw frame. Equalizing is always and in any case performed by doubling,
and can optionally also be performed by additional auto leveling.
PARALLELIZING
To
obtain an optimal value for strength in the yarn characteristics, the fibres
must be arranged parallel in the fibre strand. It is mainly the draw frames task
to create this parallel arrangement. It fulfills this task by means of the draft,
since every drafting step leads to straightening of the fibres. The value of the
draft must be adapted to the material, i.e. to several fibre parameters,
mainly:
§ The staple length;
§ The mass of the fibres;
§ The volume of the strand;
§ The degree of order (parallel
disposition).
BLENDING
In the spinning process every doubling
produces simultaneous blending especially the 8-10 doublings on the draw frame.
The doubling also provides a degree of compensation of raw material variations
by blending, which occurs simultaneously. This result is exploited in
particular in the production of blended yarns comprising cotton/synthetic or
synthetic/synthetic blends. At the draw frame, metering of the individual components
can be carried out very simply by selection of the number of slivers entering
the machine. Eg.- 70:30 blend (P:C).
DUST REMOVAL
To remove dust to the greatest
practical extent at every possible point within the overall process. Unfortunately,
dust removal can only be carried out to a significant degree. Since a large
proportion of these very small particles (dust) adhere relatively strongly to
the fibres. The draw frame is therefore a good dust-removing machine. On
high-performance draw frames equipped with appropriate suction systems.








No comments